TB IgG and TB-IGRA ELISA Kits
TB Correlative IFN-γ Release Assay (TB-IGRA) is a newly developed quantitative test kits; TB IgG ELISA kits is used to detect TB IgG antibody, both are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection.
TB Correlative IFN-γ Release Assay (TB-IGRA)
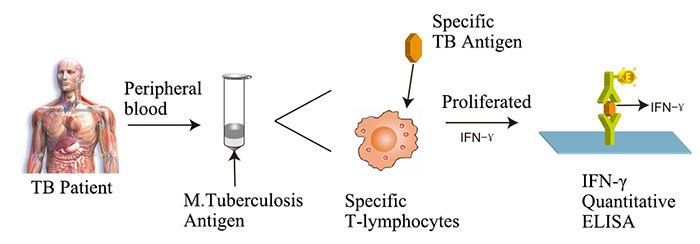
TB-IGRA ELISA kit is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for the quantitative detection of Interferon Gamma (IFN-y) that respond to in-vitro stimulation by mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in human whole blood, with detection concentration range of 2~400pg/ml. It is intended to be used as an efficient aid in the diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) infections, including both latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and tuberculosis (TB) disease.
Merits of TB-IGRA ELISA kit
IGRA measures a person's immune reactivity to M.tuberculosis. When infected with mycobacterium tuberculosis, specific T-lymphocytes will appear in the blood of the patient, which will be stimulated to proliferate and release cytokines such as IFN-γ, when they are mixed with antigens derived from M.Tuberculosis. The concentration of IFN-γ is positively related with the quantity of tuberculosis antigens.
The antigens selected for stimulation are specific fragments that pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis virus contains, while BCG vaccine and other Mycobacterium don't contain. This greatly improves the specificity of the TB-IGRA Assay kit. And this TB Assay kit is easier to operate than other methods like PCR, bacterial culture and SPOT.
This TB-IGRA ELISA kit can be used in the following realms:
- Active tuberculosis detection;
- Latent tuberculosis detection;
- TB therapeutic effect monitor;
- Medication instruction;
- Prevent TB cross infection.
Tuberculosis and TB Test Kits
Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB or TB). It is a small bacillus that can withstand weak disinfectants and can survive in a dry state for weeks. TB is transmitted almost exclusively by aerosol from the respiratory secretions of patients with active M. tuberculosis.
As present, Tuberculosis remains an important socio-economical and medical problem throughout the world. The early detection of tuberculosis disease will help to reduce and chance of further spread, and will help to the cure of the infected. In this way, the in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) TB testing devices are contributing to the control of tuberculosis spreading.

 Atlas Link Technology Co., Ltd
Atlas Link Technology Co., Ltd